Table of Contents
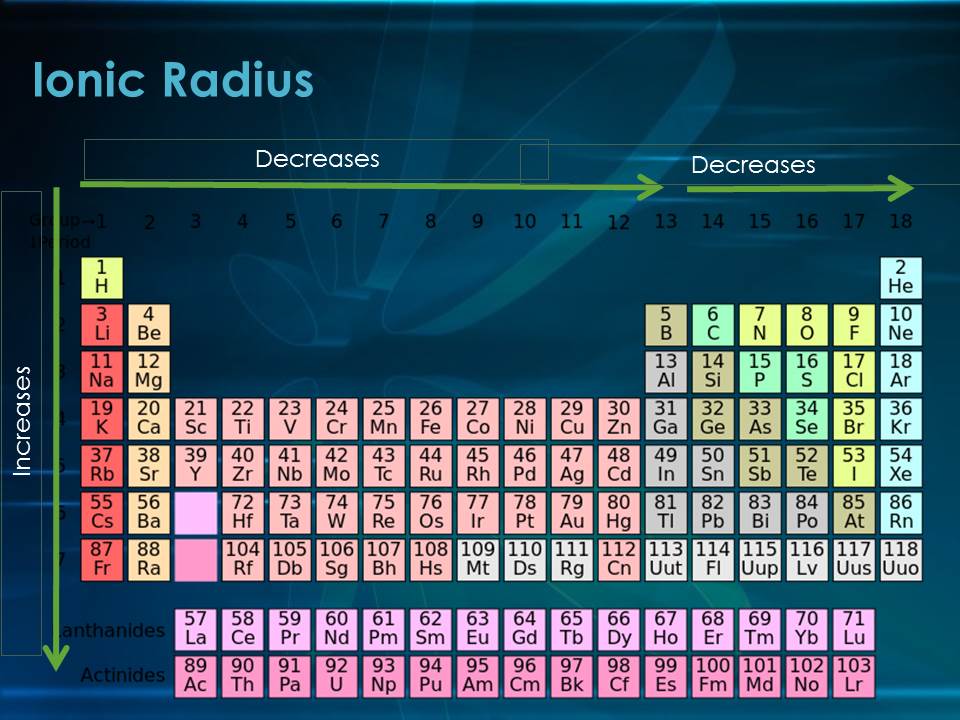
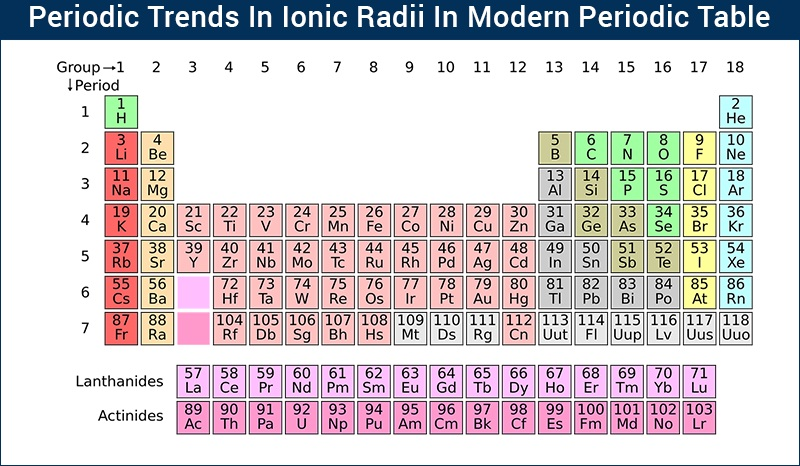
The trendionic radius trend is a crucial concept when studying the periodic table. It helps us understand how the size of ions changes as we move across different groups and periods. The ionic radius is the distance from the center of an ion to its outermost electron.
By learning the trendionic radius trend, we can see how elements behave differently based on their position on the periodic table. This trend helps us understand not only the size of ions but also their reactivity and how they form bonds with other elements.
What Is the Trendionic Radius Trend and Why Does It Matter

The trendionic radius trend is an important concept in chemistry that helps us understand how ions change size. Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons. The trend shows how the size of these ions changes when moving across a period or down a group on the periodic table.
In general, as you move down a group in the periodic table, the ionic radius increases. This happens because each new element adds another electron shell, making the ion larger. On the other hand, as you move from left to right across a period, the ionic radius decreases.
Explaining the Trendionic Radius Trend: How the Size of Ions Changes
The trendionic radius trend is linked to the number of electrons and protons in an atom or ion. When an atom becomes an ion, it either loses or gains electrons. This change in electron number affects the size of the ion. For example, when a metal atom loses an electron to become a positive ion (cation), the ion becomes smaller.
On the other hand, nonmetals often gain electrons to become negative ions (anions). As a result, the ion becomes larger. This happens because the added electrons create more repulsion between the electrons, causing the electron cloud to expand.
How Moving Across the Periodic Table Affects the Trendionic Radius Trend

As you move across a period from left to right, the trendionic radius trend shows that the ionic radius decreases. This might seem strange at first, but the explanation is simple: the number of protons in the nucleus increases, which pulls the electrons closer to the center.
This trend is particularly important when comparing metals and nonmetals. Metals tend to lose electrons to form smaller cations, while nonmetals gain electrons to form larger anions.
The Difference Between Ionic and Atomic Radius: What You Need to Know
The ionic radius and atomic radius are closely related but not the same. The atomic radius is the size of a neutral atom, while the ionic radius refers to the size of an ion. Ions can be larger or smaller than their neutral atoms. For example, when an atom loses electrons to become a cation, it becomes smaller.
The trendionic radius trend helps explain these changes in size. As we move down a group on the periodic table, the ionic radius increases, and as we move across a period from left to right, the ionic radius decreases.
How the Trendionic Radius Trend Helps Us Predict Chemical Behavior
The trendionic radius trend plays a significant role in understanding how elements react with one another. When elements form ions, their size can determine how easily they bond with other elements. For example, ions with smaller radii tend to form stronger bonds because the nucleus can pull the electrons closer, creating a more stable ion.
This trend also affects the reactivity of elements. Elements with larger ionic radii may be less reactive because their electrons are farther from the nucleus, making it harder for them to participate in chemical reactions. On the other hand, elements with smaller ionic radii are more reactive and can form stronger bonds.
Conclusion
Understanding the trendionic radius trend is essential for grasping how ions behave in chemistry. By knowing how the ionic radius changes across periods and groups, we can better predict how elements will react and bond with others. The size of an ion is not just an interesting fact; it plays a huge role in how substances form compounds and participate in chemical reactions.
Overall, the trendionic radius trend helps us make sense of the periodic table and how elements interact. Whether you’re learning about the size of ions or how they form bonds, understanding this trend gives you the tools to dive deeper into the world of chemistry. Keep exploring and you’ll find that these trends are not just useful but also fascinating!
FAQs
Q: What is the ionic radius trend?
A: The ionic radius trend shows how the size of ions changes across periods and down groups on the periodic table. Ions get bigger as you move down a group and smaller as you move across a period from left to right.
Q: Why do ions get bigger as you move down a group?
A: Ions get bigger because each new element adds an extra layer of electrons, making the ion larger and increasing the distance from the nucleus to the outer electrons.
Q: What happens to the ionic radius across a period?
A: As you move across a period from left to right, the ionic radius decreases. This happens because more protons are added to the nucleus, which pulls the electrons closer, making the ion smaller.
Q: How does the ionic radius differ from atomic radius?
A: The ionic radius is the size of an ion, while the atomic radius is the size of a neutral atom. Ions are either smaller or larger than their neutral atoms depending on whether they lose or gain electrons.
Q: Why is understanding the ionic radius trend important?
A: Understanding the ionic radius trend helps predict how elements will bond and react with other elements. It’s crucial for understanding chemical behavior and reactivity.